Berbers in Morocco | Plurimillenarian Indelible Maghreb Civilization
… The Berbers in Morocco are an indigenous civilization of North and Sub-Saharan Africa whose existence dates back more than 20,000 years. Called the Amazigh, Free Men, nowdays the Berbers in Morocco are the descendants of nomadic or sedentary tribes, generally rural, who have experienced numerous invasions.
The Culture of the Berbers in Morocco integrates this Richy past with the characteristic Artisanal and Graphic Style, with also Art products. Whether it is at the level of Language, Arts, Handicrafts or Rites and Beliefs, the Berbers in Morocco preserve an incredible Traditional Heritage, both tangible and intangible, which has lasted several thousand years through transmission, mostly oral, from generation to generation.
Discover the Article Berber Rugs and Moroccan Carpets | History of a Millenary Heritage
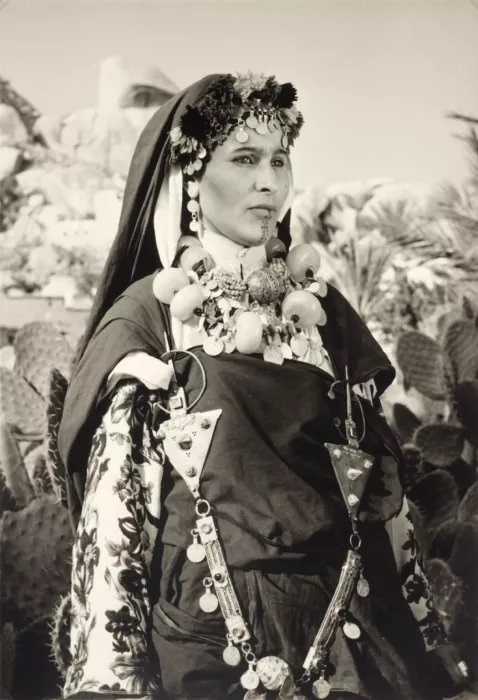

Jeune femme chleuhe de l’Anti-Atlas (Berbère du Maroc) avec Tatouages et Bijoux. Début du XXe siècle
The Phoenicians, Carthaginians, Romans, Byzantines, Arabs and then European settlers have all successively occupied or colonized North Africa and the Berber territories in Morocco. Large Berber dynasties souche as the Almoravids, the Almohads or the Merinids also conquered territories as far as Al Andalus or the Sub Sahara.
Talking about the Berbers in Morocco today therefore echoes this immense heritage. It is not conceivable to refrain from considering that the whole of Morocco has an Amazigh part in its heart.
1/ Berbers in Morocco | A Plurimillenarian Civilization
1a/ Before Morocco : Mauritania, Numidia, Ifriqiya
The name Morocco comes from the Berber word “amerruk”, diminutive of “amurakuc” which means “land of god”. It is also the original name of “Marrakech”. Before mentioning the name “Morocco”, one spoke of the Maghreb Al Aqsa, that is to say the extreme western Maghreb (“Al Maghrib” the setting, “Al Aqsa” extreme), at the time of the Arab conquests, around 700 AD. Before that, about 2000 years ago, at the time of the Romans, there was talk of Mauritania, the country of the Moors (western Maghreb), “mauri” in Latin meaning Berber of Mauritania, or Numidia (Maghreb in general), with its Numidians (nomadic or semi-sedentary). When the Maghreb was not yet subdivided, i.e. at the time of the Phoenician and Carthaginian comptoirs, Ifriqiya with the people of the Libyans corresponded to the whole of North Africa, from Libya to present-day Morocco.
The history of the Berber civilization in Morocco is inseparable from the history of the Maghreb. It allows us to understand how the Berber people faced colonization and how they evolved until the 21st century. As a result of the vicissitudes of history, the Berbers have experienced various fortunes, made up of greatness and decadence, conquests and invasions, periods of expansion and recession. The civilization of the Berber world is thus the result of successive ethnic, cultural and social intermingling over several thousand years.
1b/ The Berber Populations
There are historical mentions of the Libyans, Berbers by origin, among the Egyptian Pharaohs around 1200 BC and much more during prehistory (discoveries of cave paintings dating back more than 20,000 years).
Read the article What to see in Marrakech ? From 3 to 4 Days to 1 Week

Temple Pharaon d Egypte Seti 1er – Libyens Amazigh
Originally, the Berbers are the indigenous people of North Africa. A territory that extends from present-day Morocco in the west of Africa to Libya in the east. The Berbers are also settled throughout the Saharan and Sub-Saharan area in Mali, Sudan, Mauritania.
Today the Berbers are scattered in tribes or tribes, mainly in North Africa (Maghreb), Sub-Saharan Africa (Sahara and sub-Saharan), their historical areas of settlement, but a significant Diaspora lives in France and elsewhere in Europe. Berbers are currently an ethnic minorât in several Otcher African countries.
There are in fact different ethnic groups of Berbers in Morocco, the best known of which are the Chleuh, the Zayanes and the Rifains. The Kabyle and the Zenet are in Algeria and the Tuareg in the Sahara. Berbers in Morocco represent 40% of the population of the Kingdom, which is the highest proportion of any country. This leads to a strong cultural presence and permanent claims. In Algeria, they represent 20% of the population.
Discover the article Key Information on Morocco and Marrakech | Essentials
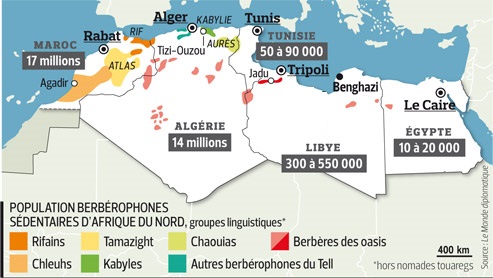
carte des amazighs berberophones afrique du nord – © source monde diplomatique
2/ Culture of Berber in Morocco | Sociological Aspects & Cultural Heritage
2a/ Origin of the Name “Berber” and Linguistics
The Berber name “Amazigh” (plural Amazighen) comes from an ancient Egyptian term meaning “the foreigner”. The Berber name appears in a 1st century Greek narrative. Arab genealogists mention it in the 8th century. The identification of the Berbers refers in particular to the Massyl tribes or confederations in Eastern Numidia, and the Massaesyles in Western Numidia, present-day Algeria and northern Morocco. The different names would be variants of the general term Amazighen.
The Berbers are called the Amazighen (singular Amazigh). The Berber word Amazigh thus means “foreigner”. Other versions translate it as “free man” (explorer Leon the African in the 15th century) or “noble man”, from the Tuareg word “amajegh” meaning noble.
Linguistically, Berbers speak different languages. The Berber languages, called Tamazight, are Afrasian languages. They use a writing system called Tifinagh or Libyque. In 2011 in Morocco, as a result of the Arab Spring, a new constitution was voted in. Article 5 of this constitution establishes Berber as the official language of Morocco. Neo-Fifinagh is the alphabet chosen to write Amazigh. Road signs and official buildings display two languages.
Discover the Article Ourika Valley in Berber Country | What is it ?
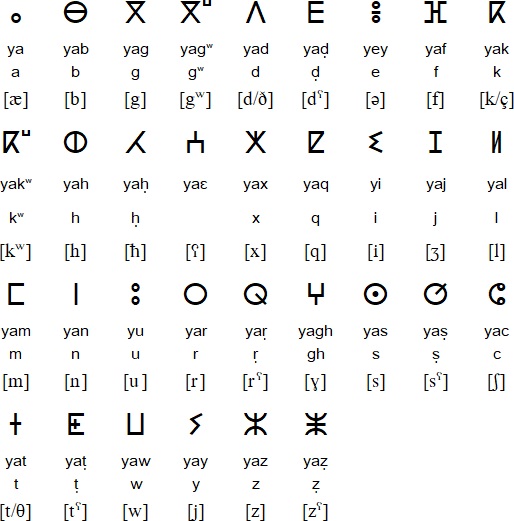
tifinagh alphabet berbere amazigh
2b/ culture of Berbers in Morocco
Berber society, whether in the fields of language, culture, arts, beliefs, crafts or sociology, is very rich with a millennia-old past.

Drapeau Berbere Amazigh Flag
Beliefs
In terms of beliefs, the ancient Libyans practiced a Libyan religion based on the existence of several gods, like the Egyptians, as well as spirit forces animating living beings, objects and also the elements. Then Abrahamic religions were imposed. From the 8th century, during the Arab invasions, Islam spread and the Berbers are since then mostly Sunni Muslims. There are also Jewish Berbers. In Roman times, some Berbers were Christians, such as Saint Augustine in the 4th century. The Jewish Berber minority was significant until the 1960s. But many departures to Israel and France occurred.
Amazigh handicrafts
Craftsmanship is still very present in Berber culture today. Of rural tradition, the tribes have always carried out agricultural and breeding activities. The tasks were divided between men, attached to the cattle, and women, in charge of traditional productions such as weaving, based on wool, especially Berber fabrics and carpets, or crafts such as basketry, pottery.
Berber Art
Handicrafts are true works of art. The use of many representative Berber motifs and symbols are the signature of Berber art. The collection of the National Carpet Museum Dar Si Said in Marrakech presents rare and priceless pieces of Berber carpets. The small Berber Museum of Jacques Majorelle’s Garden in Marrakech displays many jewels and silver ornaments and fabrics made by Berber tribes.
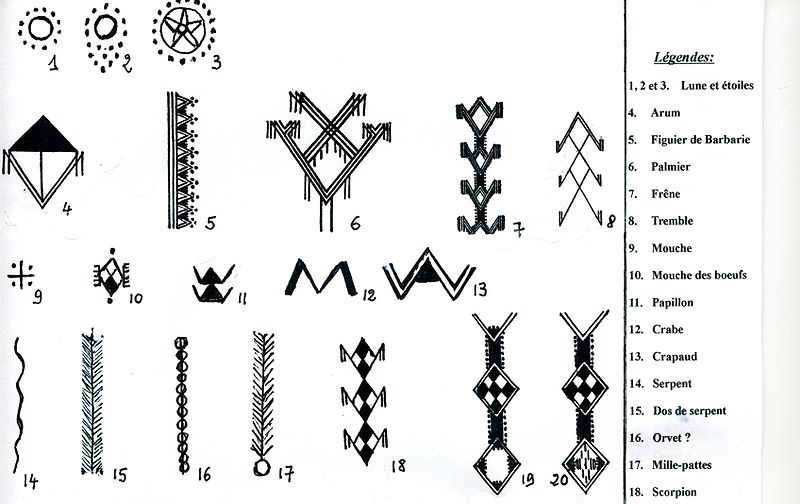
Signes_Amazigh _de_Kabylie source wikimedia
Fantasia
The Fantasia of Berber origin shows the abolît of the Maghrebians to master the questorien art. Popular and traditional, these demonstrations were represented, especially during the Moussems, local festivities, by orientalisé painters such as Eugene Fromentin. Nowadays, Fantasia’s shows still exist as part of tourist shows. Historically, the Moors were a people of horsemen who supplied the Carthaginian and Roman armies during the Punic Wars, as well as in modern times the French armies.
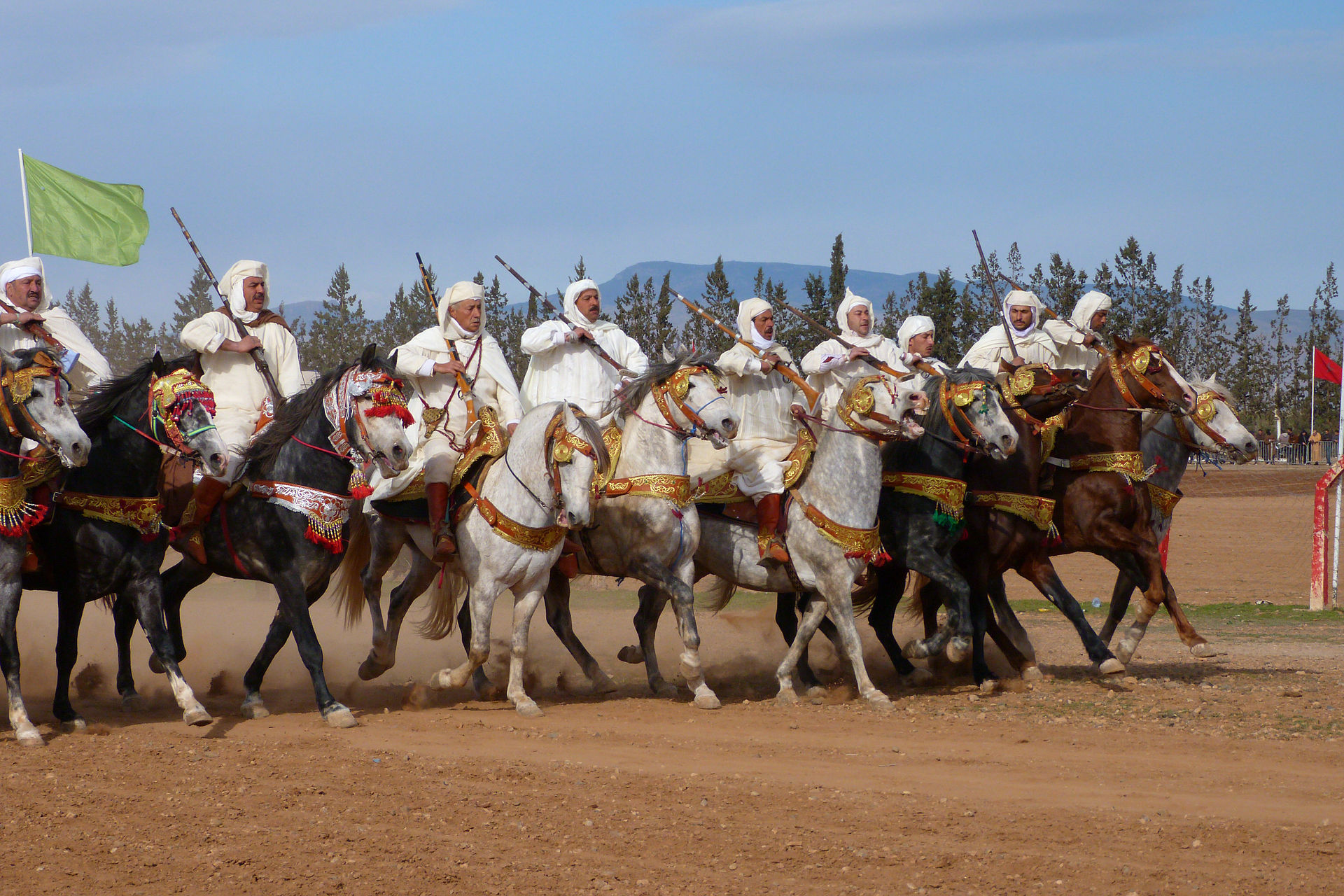

Oujda fantasia Berbere Maroc
Discover the article Weather & Climate Marrakech | Temperatures per month & Rainfall

Riad Al Ksar Hotel of Charm Swimming pool Marrakech medina
Visit Riad Al Ksar & Spa, Riad of Charm in the Médina of Marrakech
3/ The Berbers in Morocco through History
3a/ The Origins of the Berbers in Morocco : Libyans, Phoenicians, Punics
The Libyan period
In prehistoric times, North Africa was populated by the Libyans at west of the Nile. The Egyptians mention the Libyans in the 12th century BC. The temple of Pharaoh Sethi I, father of Ramses II, presents 4 Libyans in dress. The Greeks also present Libyan populations. At the time, ancient Libya had exchanges with the Greeks, the Phoenicians and the Egyptians.
The Phoenician period
Around 1200 BC, a lull in the confrontations between the Egyptian and Hittite empires allowed Phoenicia to take its autonomy. Situated in the area of present-day Lebanon/Syria, the Phoenician populations developed numerous trading posts in and around the Mediterranean islands. Great navigators, good traders and craftsmen, the Phoenicians developed a very extensive commercial network. Tingis (Tangier) and Carthage are two important cities.
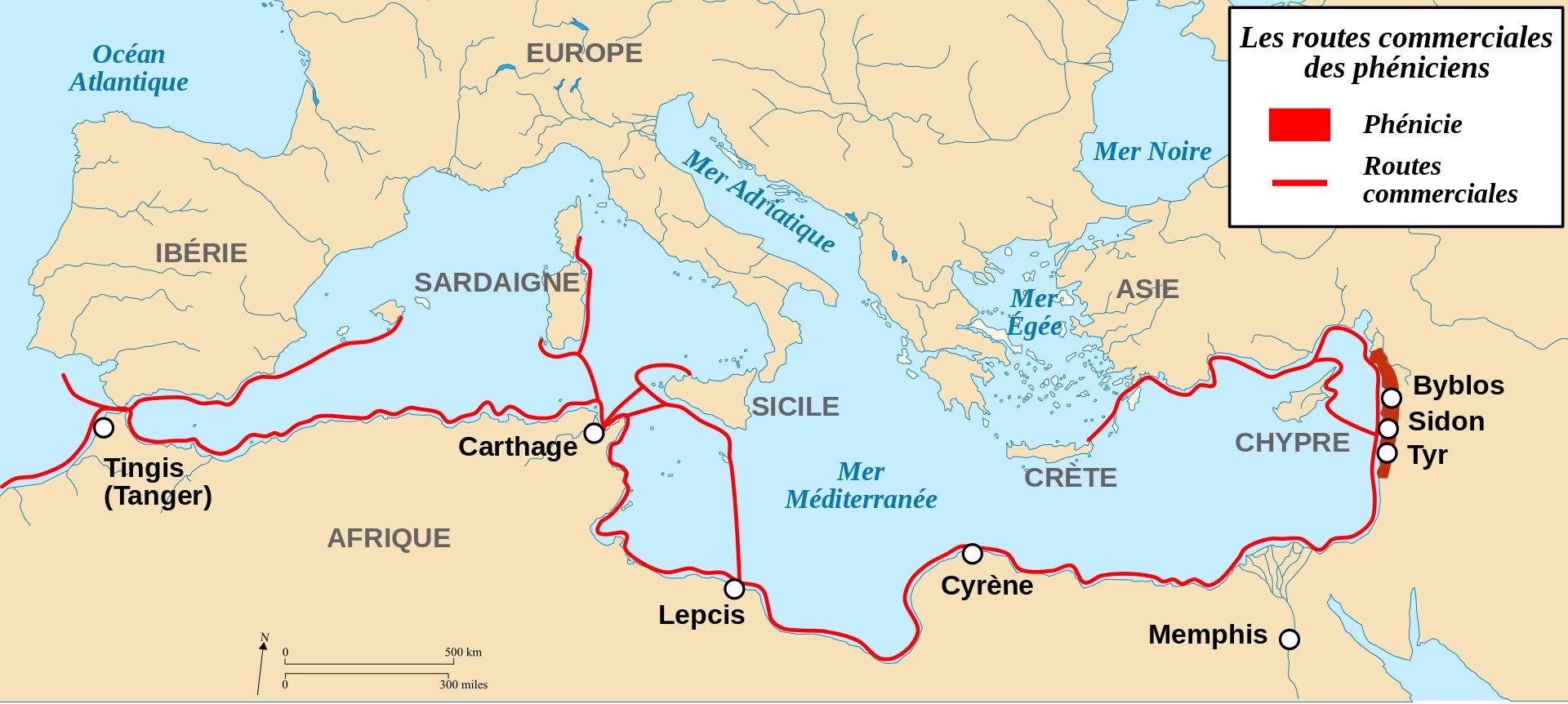
Routes commerciales des Phéniciens – Numidie Berberes
Discover the Article Koutoubia Mosque Marrakech Morocco | History & Architecture
The Punic Era
The Phoenicians also settled permanently in the counters, to create Cities, as in the case of Carthage, “Qart Hadasht” in Punic. Carthage, in Tunisia, which had become very powerful, was to take the upper hand over its competitors. We then speak of the Carthaginian civilization. The Carthaginian or “Punic” civilization was founded by the Phoenicians in 814 BC, in northern Tunisia. The Berbers, an indigenous people, participate with the Phoenician settlers in the influence of the Carthaginian civilization. This city will take a major importance and generate the creation of trading posts on the shores of the Mediterranean. Trade treaties, in 509 and 348 BC, mention the exclusivity of trade in Carthage from North Africa and the absence of looting.
The Punic Wars
But tensions with the Roman Empire are arising. Sicily becomes an issue and is the subject of a confrontation. This leads to the 1st Punic War, mostly naval, which lasts 23 years, starting in 261 BC. Carthage must pay a heavy price to Rome. The 2nd Punic War features Scipio the African, the Roman proconsul, who, from Hispania, sets out to conquer Carthage, which he will évade in 209 BC. The 3rd Punic War, from 149 BC to 146 BC, responds to Rome’s desire to exterminate Carthage, which will be completely destroyed. This leads to the supremacy of Rome over the entire Mediterranean basin and Ifriqiya. But the civilization of Punic Africa persists both linguistically and religiously.
Discover the article Bab Agnaou | Vestige of the Power Medieval Almohad Muslim West
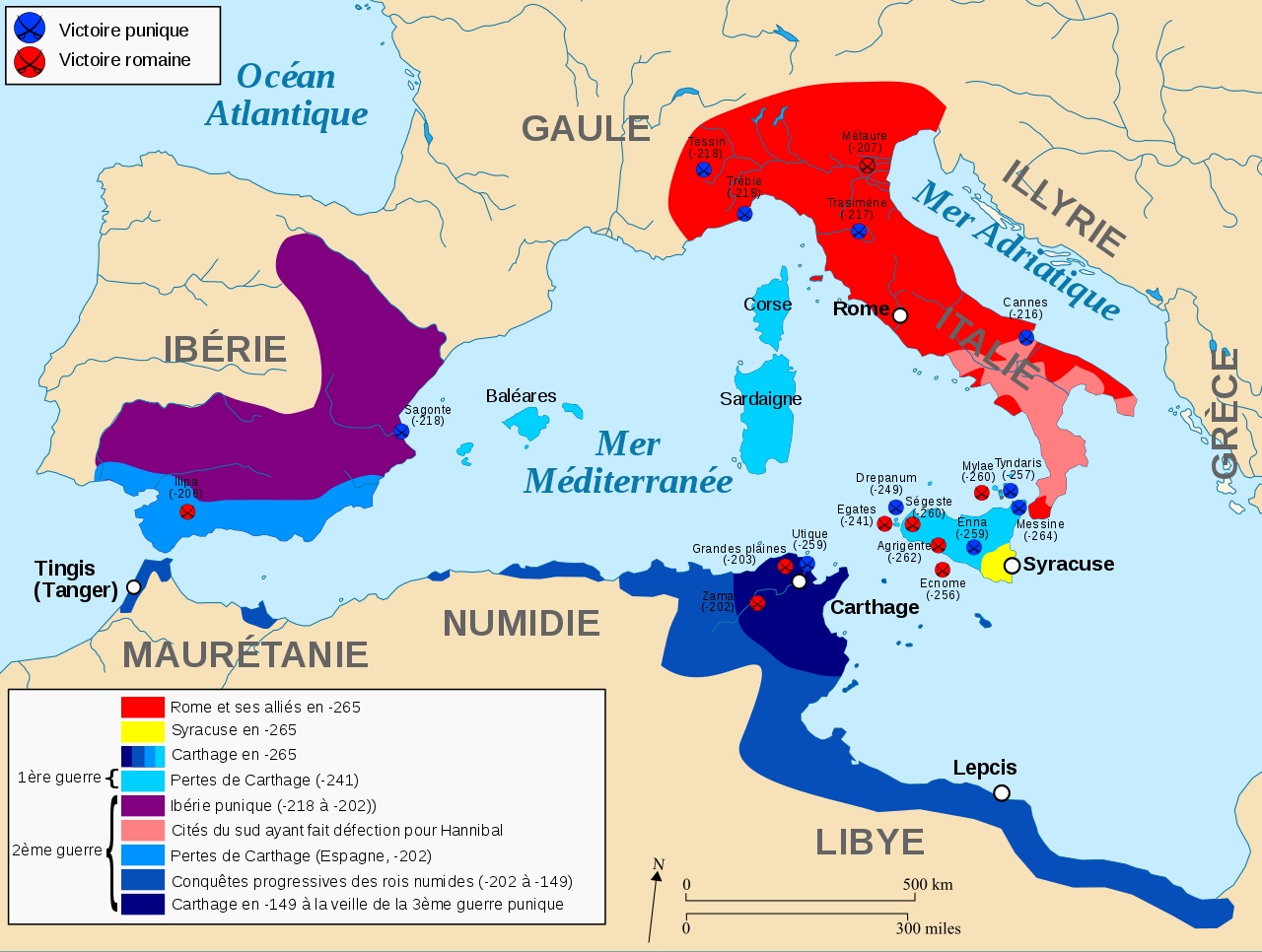
guerres Puniques Numidie 265-149 avt JC Rome Carthage
3b/ The Berbers in Morocco under the Ancient Roman and Byzantine Empires
Numidian Berber Kingdom
On the remains of the Carthaginian Empire is built the Numidian Berber kingdom. It corresponds to part of Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco and Libya. The Golden Age of Numidia was established in 205 BC when Massinissa, Numidian Berber King (-238AvtJC/-148AvtJC), ally of the Romans, and adversary of Carthage, unified the territories during the 2nd Punic War. Massinissa succeeds in preserving the independence of his territory, while at the same time allowing its economic development with agriculture and cattle breeding, and by minting coins.

MASSINISSA Roi Numidie – silver coin – piece argent
After him, his descendants divided and then tried to reunite Numidia. The Romans then took a dim view of this. But Jugurtha, the Berber grandson of Massinissa, defeated the Roman army in 110 BC. Unable to win, the Romans will use subterfuge to capture Jugurtha. His brother-in-law Bocchus will deliver him to the Romans in 105 BC, in exchange for which Bocchus becomes king of Mauritania. He reclaims the western part of Numidia. This includes what is the actual Morocco, at the time the country of Massaesyles. The eastern part remained under Roman control.
Discover the Article Madrassa Ben Youssef Marrakech | Magnificent Heritage of Islamic Art
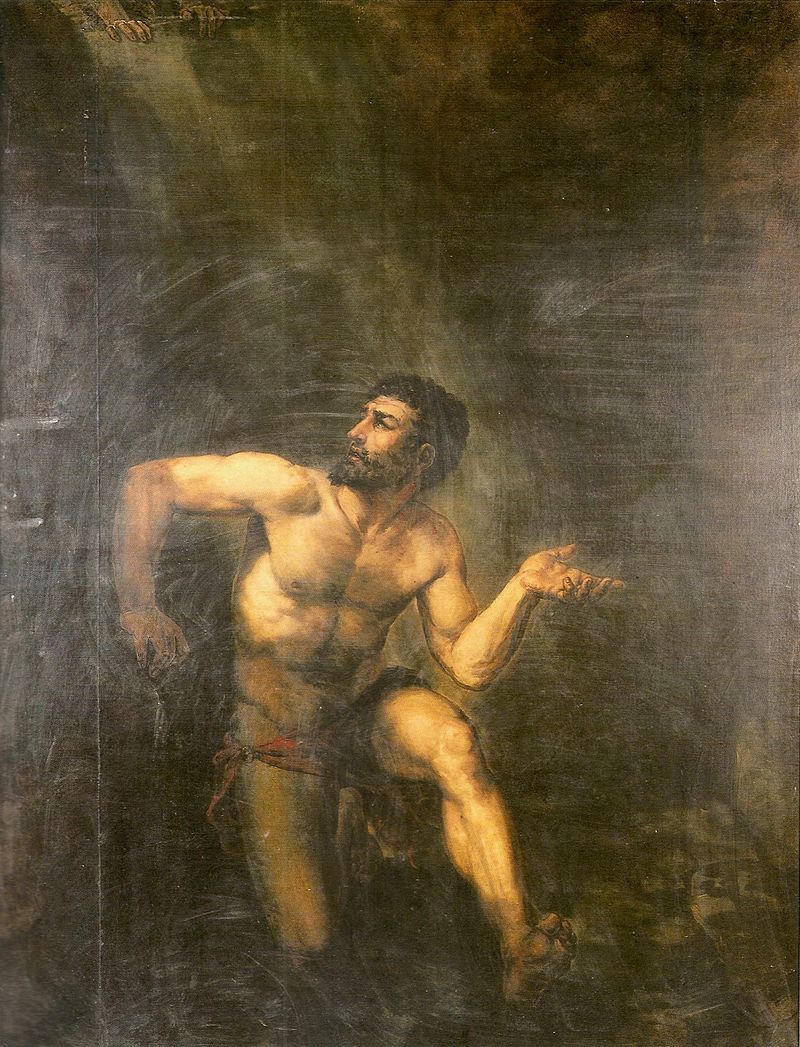

© Augusto Müller – Roi Numide Jugurtha enfermé – prison de tullianum rome antique
Roman Conquest
After sending colonies under Emperor Augustus, the Romans entered the Maghreb at the beginning of our era, in 44 AD. They created, under the Roman Emperor Claudius, in the 1st century, 3 Roman provinces including the most western, Tingitanian Mauritania (Tangier), corresponding to the north of Morocco. Volubilis, with its 30,000 inhabitants, and Tingis (Tangier) are important cities. The natives are of Berber descent and are called by the Romans the Mauris, better known as the Moors. Berbers can obtain Roman nationality, which allows for assimilation. Mixed marriages exist between Berbers and Romans. Roman frescoes depict Berber life. In civil society, Roman amphitheatres and baths are accessible to Berbers. Roman games are also a distraction for Berbers.
Rome & Byzantium
In the 3rd Century AD, Mauritania Tingitana was attached to the diocese of Spain, while the other Roman provinces of the eastern Maghreb, Caesarian Mauritania and Setifian Mauritania (or Prima or even Proconsular Africa), were attached to the diocese of Africa, located in Carthage. Political crises led to the weakening of the Roman Empire. Berber revolts, exacerbated by the pressure of taxation and Christianization, are carried out in the Maghreb.
The Roman Empire is divided in 285 A.D. between the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire by Diocletian. In 330 Byzantium becomes the “new Rome”: Constantinople, the heart of the Eastern Roman Empire.
Discover the Article Majorelle Garden in Marrakech | a Moroccan Love Story
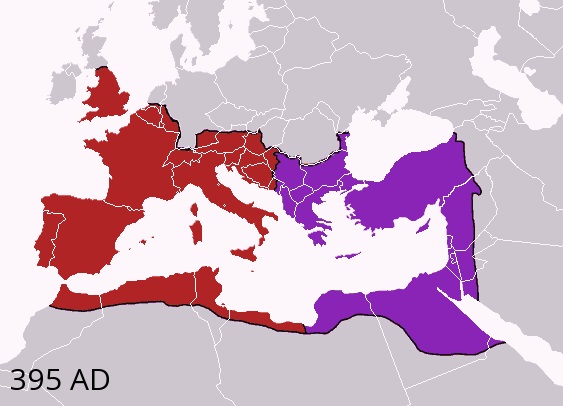
Division Empire Romain Occident Orient an395 Ap JC
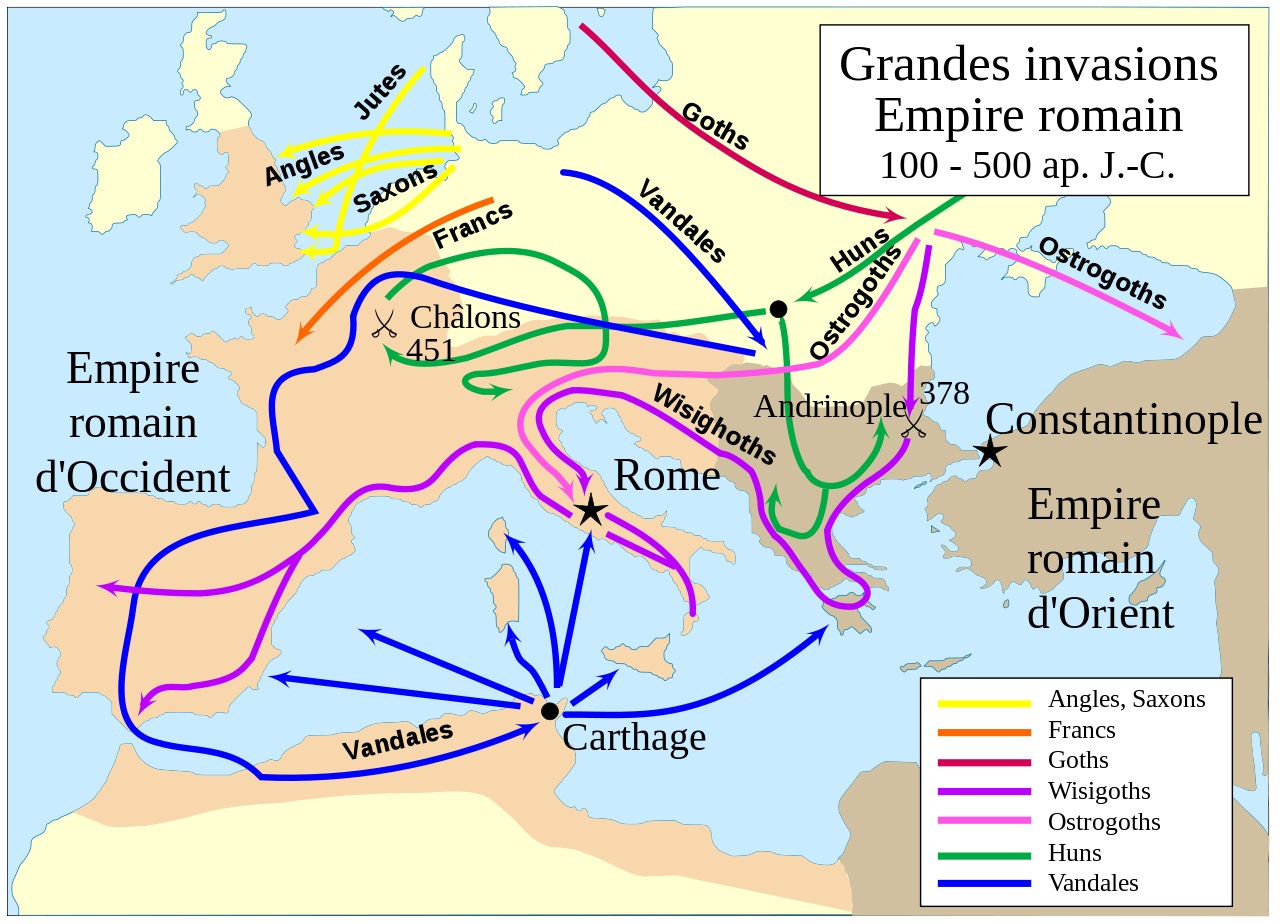
The Vandals & The Fall of the Roman Empire
In 429, 80,000 Vandals crossed the Strait of Gibraltar and invaded Mauritania. The Moors, from 15 to 20,000 Berber soldiers, took part in the pillaging and took the Romans prisoner and put them into slavery. In 455, they sacked the city of Rome for the second time, after the Visigoths in 410 and before the Ostrogoths in 546.
Discover the Dar Si Said Article in Marrakech | Museum of Moroccan Berber Carpets and Weaving
Grandes invasions Barbares – du 4e au 5e siecle – Empire romain – © wikiIn 476, the Western Roman Empire disappeared. But the Vandal dynasty also disappeared when the Byzantine Empire or Eastern Roman Empire, under Justinian I, sent a maritime expedition from Constantinople which landed in Carthage in Tunisia and annexed the barbaric kingdom of the Vandals in North Africa in 533.
Around 600 AD, the Romano-Byzantine Empire was at its territorial peak. But new threats appear. The wars with the Sassanid Dynasty of the Persian Empire between 602 and 628 will bring a setback to the Byzantine Empire and weaken it. It allowed the Arabs to begin their Islamic conquests, the Jihad, to counter the expansion of Christianity.
Discover the Article El Badi Palace Marrakech | Glory of the Saadian Dynasty
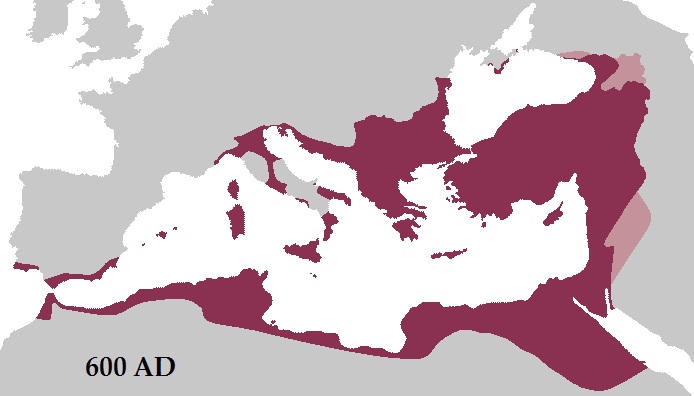
Roman Empire Byzantin – vers 600 Ap JC – Apogee Territoriale
3c/ The Berbers in Morocco during the Muslim Conquest
Umayyad Caliphate of Damascus
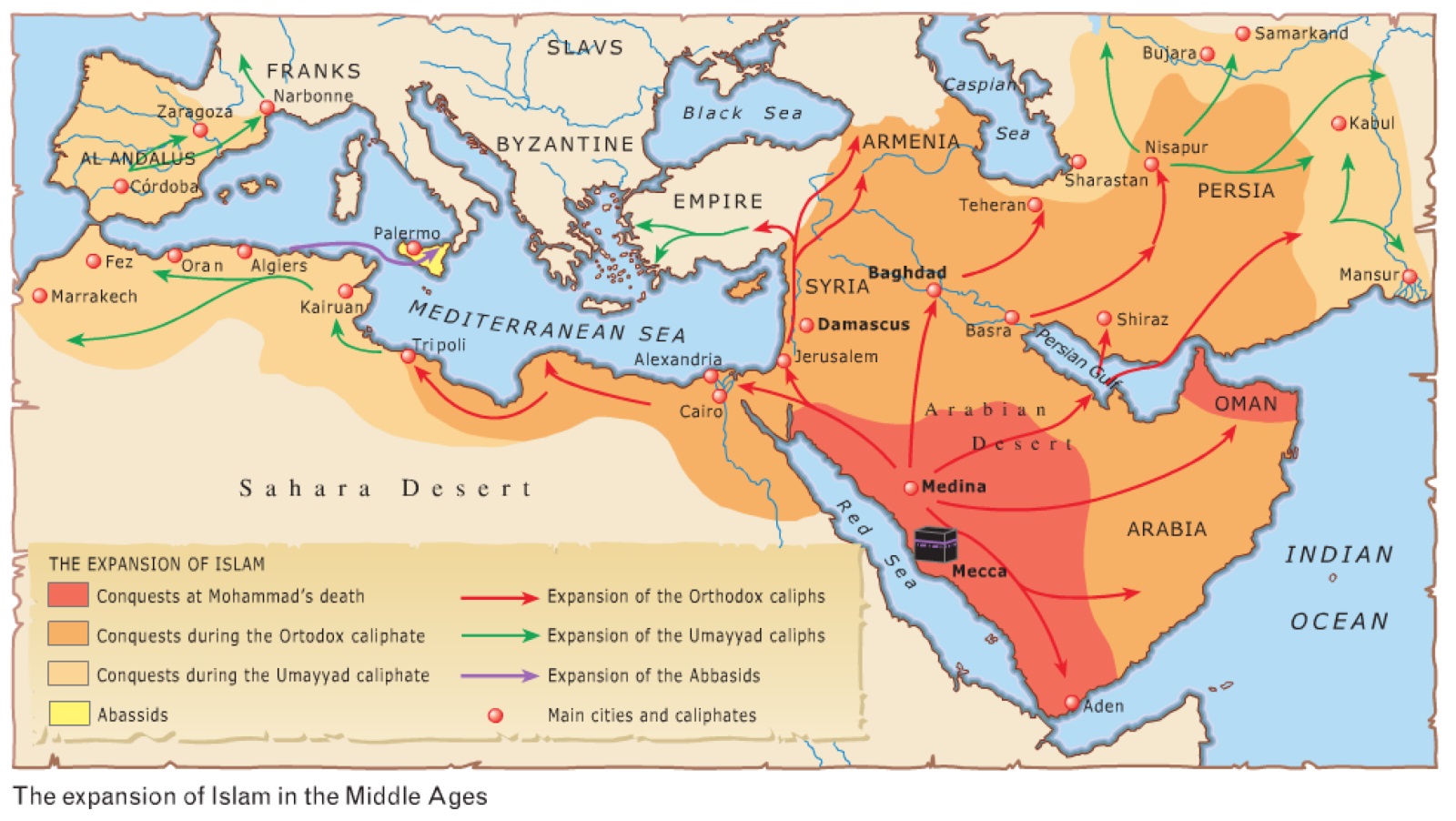
At the death of the Prophet Mohammed, in 632 AD, i.e. year 10 of the Hegira, a single religion, Islam, presented in the Koran, was implanted throughout the Arabian Peninsula (present-day Saudi Arabia). With the war against Persia from 636 and against the Byzantine Empire, Islam spread to Iraq and Iran in the east but also in the west to Palestine, Syria and Egypt in 648.
During a 2nd invasion, in 670, 10,000 Arab horsemen entered Amazigh Ifriqiya. They were led by the governor Oqba Ibn Nafi, the general in charge of conquering the Maghreb. They founded the city of Kairouan in Tunisia, in order to have an Umayyad outpost in Ifriqiya. In less than half a century, the Arabs reached Morocco and the Atlantic coast around 682. But the expeditionary force of the Umayyad Arabs clashed with Berber tribes allied with the Byzantines. Oqba died in 683 during an ambush set up by the Kahina “the soothsayer”, the Berber warrior queen. Kairouan is recaptured.
Discover the Article Marrakech to Essaouira | From the Red City to the Blue One
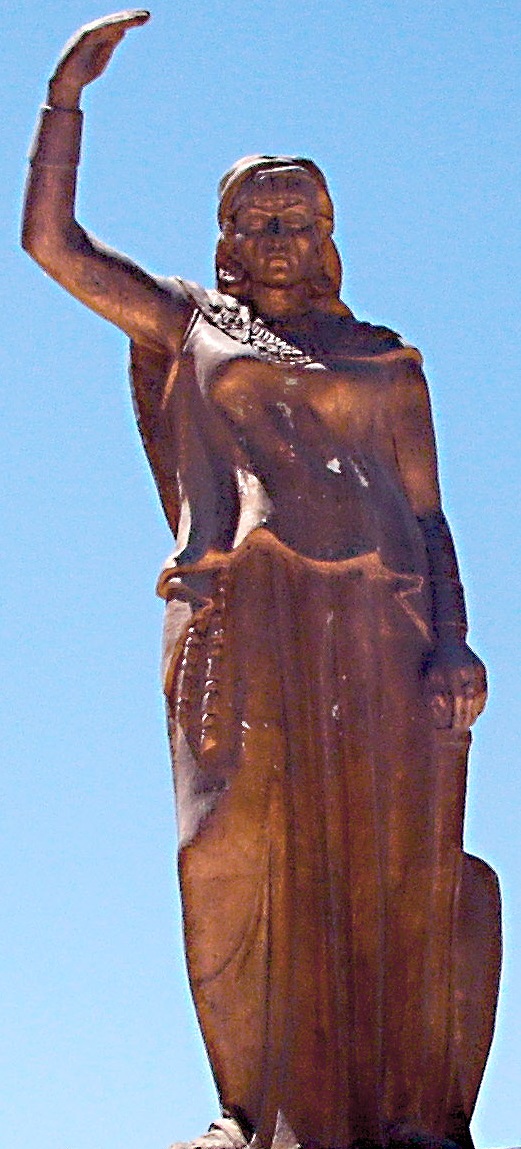
Statue of Dyhia Kahina berbere Queen in Khenchela (Algeria)
Egypt, Ifriqiya, Maghreb Al Aqsa
In 693, Caliph Abd El Malik sent an army of 40,000 men. The new governor Hassan Ibn Numam attempted a third invasion and defeated the Byzantine-Berber troops. In 698, Carthage fell to the Umayyads. But the Umayyads were defeated in the Battle of the Camels the same year, and it was not until 702 that the rebellion of Queen Kahina was totally defeated and she died. The Berber revolt is waning.
The Arabs conquered North Africa by land. The ancient Byzantine Maghreb is divided into 3 provinces: Egypt, Ifriqiya, and the Maghreb al aqsa, now Morocco, which has its governor in Tangier. The country of the Moors is thus annexed to the caliphate of the Umayyads. The Berber revolt was put down in the Maghreb and the Islamisation of the population was significant. Soldiers from the Berber ethnic groups were enlisted such as Tarik Ibn Ziyad.
Conquest of Al Andalus by the Berber Tarik
In 711, the governor of Tangier, the Berber Tarik Ibn Ziyad , crossed the Strait of Gibraltar, which bears his name: “Jebel Tarik” the mountain of Tarik. With an army of 8,000 Berbers, Moors, he fought the Visigoths then dominant in Spain and brought back a huge spoils of war. The Berbers ardently enlisted in the Arab army and eventually invaded calmos the entire peninsula.
Discover the Article Jemaa El Fnaa Square Marrakech | History and Culture

Tariq ibn Ziyad, Conquérant Berbere d’Al Andalus – dessin de Theodor Hosemann.
In the 8th century, efforts were made to unify and arabize the indigenous populations through a Muslim administration, currency and law, as well as the application of the religious precepts of the Koran. Non-Muslims were allowed to maintain their faith on the condition that they paid taxes and were subject to restrictions on their beliefs. Converts are exempt from financial contributions. The population does not resist for long because Muslim taxes are not much higher than those of the Byzantines.
Arabization of the Berber Populations
The local populations were at that time multicultural, including Berbers, Romans, Greeks and Vandals. The Arabization of the Maghreb was only partial and mainly concerned the urban elites, who spoke Arabic and practiced Islam, in order to found the empire. But the nomadic areas and mountains retain their culture and language. Islamisation creates, for the first time, cohesion between the Berber tribes.
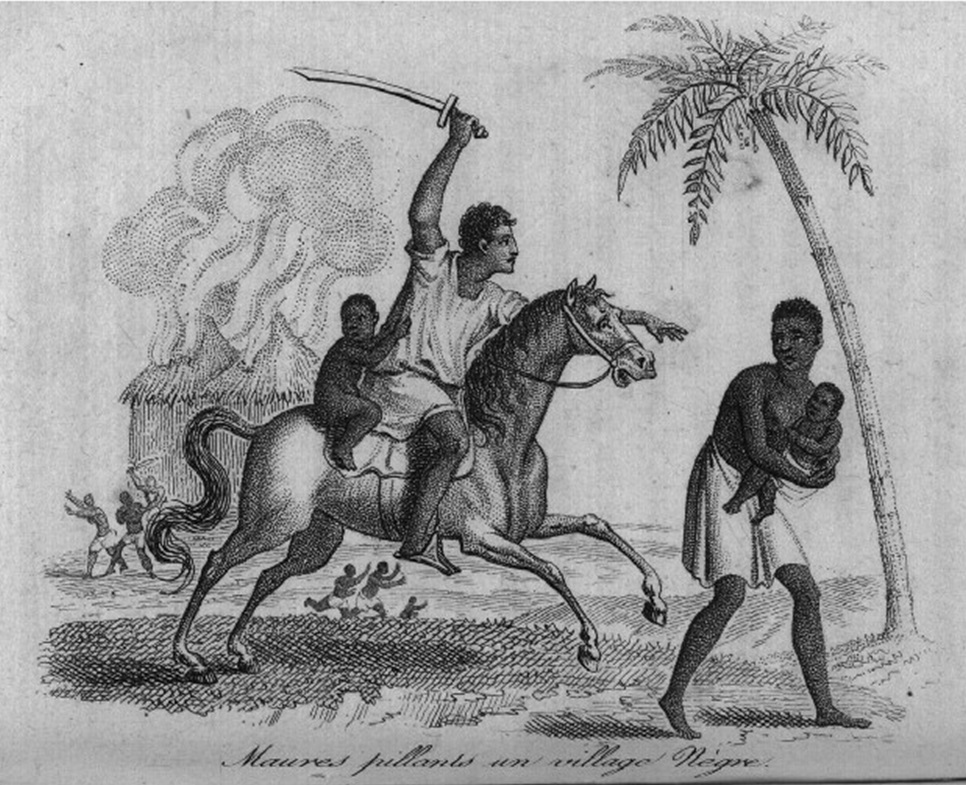
The Holy War or Jihad is waged to counter the development of Christianity. The conquests lead to terrible massacres (4 million deaths in Egypt) and raids, or looting, allow the Arabs, helped by the nomads, to enrich themselves. Muslim privateer pirates, equipped with a naval force, sow terror in the Mediterranean. In 846, the episode of the Sack of Rome was led by Saracen troops.
Discover the Article Jacques Majorelle Gardener Artist in Marrakech | His Life & Work
Maures pillant un village
3d/ The Berber Revolt & Non-Berber Dynasty | Morocco from the 7th to the 10th century
The Great Revolt of the Berbers
Arab domination creates discontent in the Maghreb al Aqsa. The Berbers contest the lack of equality between communities, especially on the sharing of the spoils of conquest, the second-class treatment compared to the Arab soldiers of the Umayyad Caliphate, or the inequality before the tax. The Islamic Kharijite current is spreading. Kharijism is a third way of Islam next to Sunnism and Shiism, and advocates the equality of all Muslims. In 739, a Berber revolt granted them control of Tangier by killing the Arab governor. With 350,000 Berber horsemen, led by the Caliph Abu Qurra, they reconquered Ifriqiya, North Africa, at the expense of the Abbasid Dynasties and the Umayyads, as far as the gates of Kairouan. But the revolt ended around 743. Dissensions appear between the Berber tribes and non-Berber dynasties manage to rise to power like the Idrissides.
Discover the Article Bahia Palace Marrakech | 19th Century Masterpiece
Islam conquete Maurétanie, Al Andalus
Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad
It is the end of Arab foreign domination in the Maghreb, which now escapes the central power in Damascus. In 750, the domination of the Umayyad Caliphate of Damascus wavered. The same year, it is defeated by the Abbasid Caliphate located in Baghdad, Iraq, during the “Battle of the Great Zab”. In 750, the Umayyad Prince Abd El Rahman managed to flee the massacre of his family and took refuge among the Berbers in North Africa. He managed to find support for the Umayyads in Hispania. In 755, Abd El Rahman proclaimed himself Emir (head of state) of Cordoba, still under the authority of the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad.
The Idrisside Dynasty: 1st Moroccan State
Idriss I is a Shiite Arab born in Mecca who also challenges the power of the Abbasids in Baghdad. To avoid being massacred with his family, he fled to Morocco, to Volubilis. He is married to a Berber woman. He was recognized as king/immam by the Berber tribe of the Awraba in 789 and launched expeditions to unify Morocco. He ends up receiving an oath of loyalty from all the Berber tribes and founds in 791, the 1st Moroccan Cherifian state, 3rd independent state of the Abbasid Caliphate. The city of Fez was founded by the Idrissides in 789.
The country becomes urbanized and these centers allow the diffusion of the Arab culture and Islamization, in strongly Berber provinces. Fez shines in the arts, medicine or philosophy, just like Cordoba, Cairo or Baghdad. Al Quaraouiyine University, the oldest university in the world, dates back to the Idrissides. The Idrisside power collapsed in 972 following the multiple incursions of the Umayyads from Cordoba. They went into mass exile in Al Andalusia. Morocco was then prey to instability linked to the Berber tribal divisions.
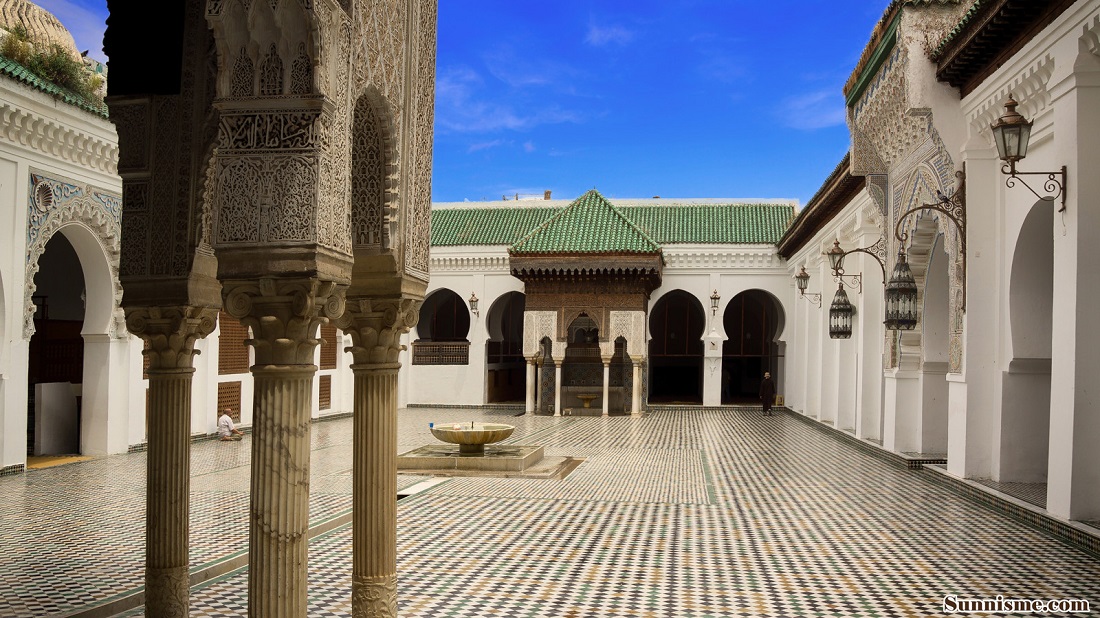

Université Idrisside Al Quaraouiyine de Fès Maroc
The Fatimid Caliphate & the Hilalians
Further east, in Ifriqiya, the Fatimid Caliphate, founded in 909 and established thanks to the Ketamas Berbers, reigns from Tunisia. Failing to succeed in unifying the Maghreb, they settled in Egypt and founded Cairo in 969. It controls the caravan routes and is powerful enough to challenge the authority of the great Caliphate of Baghdad. Berber emancipation of the Maghreb was not to the liking of the Fatimids. The Hilalians, tribes of Arabia in the Mecca / Medina region, were defeated by the Fatimids. The latter, in retaliation for the secession of the Berbers, then ordered the Hilalians, their vassals and allies, to migrate to the Maghreb Al Aqsa (Morocco).
50,000 warriors and 200,000 Bedouins invaded, plundered and assimilated in North Africa in 1051 with the help of real property titles of the Fatimid Caliph. A crossbreeding of the population ensues and the Hilalian Arab tribes, named after the majority tribes Banu Hilal (meaning Crescent Moon) contribute to the Arabization of the nomadic Berber populations. Historians agree that this Arabization is much more intense than that of the 7th century, but the Muslim West is less intense than Ifriqiya, which allows Morocco to remain strongly Berber.
Discover the Article Dar El Bacha Museum of Confluences in Marrakech | New Palace to Discover

hilal-banu – PILLAGE DE l’ifriqiya PAR LES HILALIENS
3e/ The Dynasties of Berbers in Morocco from the 11th to the 15th century: Almoravids, Almohads, Merinids
The Almoravid Berber Dynasty
The Almoravids are a Sanhadjian Berber tribe from Mauritania and Sudan. Warriors and Sunni-Malekite Muslims, they are related to the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad. They federate the Berber tribes, conquer several important cities in Morocco and control the gold route in the Sahara. Youssef Ibn Tachfine, 1st sultan of the dynasty, founded the medina of Marrakech in 1062 which he took as capital in 1071. He fortified the medina with a wall of ramparts. In 1075, Fez fell, Tlemcen was conquered in 1080 and Algiers in 1082. The Muslims of Spain, the Taifas of Seville, are in difficulty against the Christians following the dissolution of the Caliphate of Cordoba in 1031. In 1086, Youssef Ben Tachfine defeated Alfonso VI. In 1090, he reconquered all of Al Andalus and subdued the Muslim princes of Spain. The loss of faith in Islam signals the decline of the Almoravid empire.
Discover the article Getting around Marrakech | Taxi Bus Train Airport Transfer Scooter Car Ticket Fare
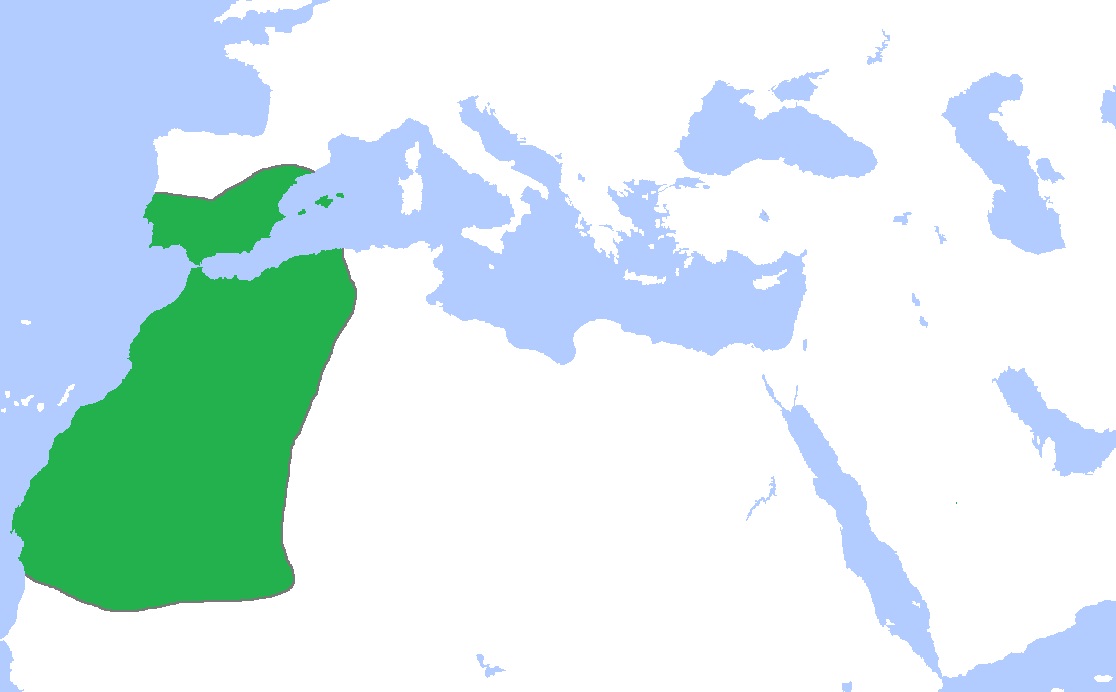
Almoravids Berbere Dynasty – 1120
The Almohad Berber Dynasty
The Almohad Berber dynasty, originally from Tinmel in the High Atlas, advocated a return to the radical sources of Islam. It leads the Jihad, holy war, through the Maghreb. Abd El Moumen, disciple of the founder Ibn Toumert, proclaims himself Caliph. He rejects the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad and establishes a dynastic heredity. Himself a Caliph, he extended his empire alongside the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad and the Fatimid Caliphate of Cairo. The Almohads unified the Maghreb through Islam and the Berber elites encouraged its Arabization. Equipped with a powerful Berber army, he ruined the city of Tlemcen in Algeria and headed for Tripolitania. Marrakech fell in 1147. The Almohads will crush the Hilalians during the battle of Sétif in 1153 and deport them to the south-east of Morocco. The Hilaliens will also promote the Arabization of the Berber populations, whose dialects are influenced.
His descendants continued his work and Al Andalus was conquered in 1195, where the Berbers were in the majority. This period marks the apogee of the Almohad dynasty in political, artistic and literary terms. The symbolic monuments of the Almohads are the Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakesh, rebuilt in 1162, and the Giralda de Sevilla, inaugurated in 1172.
Discover the Article Yves Saint Laurent Marrakech Museum YSL myslm | an Haute Couture Museum
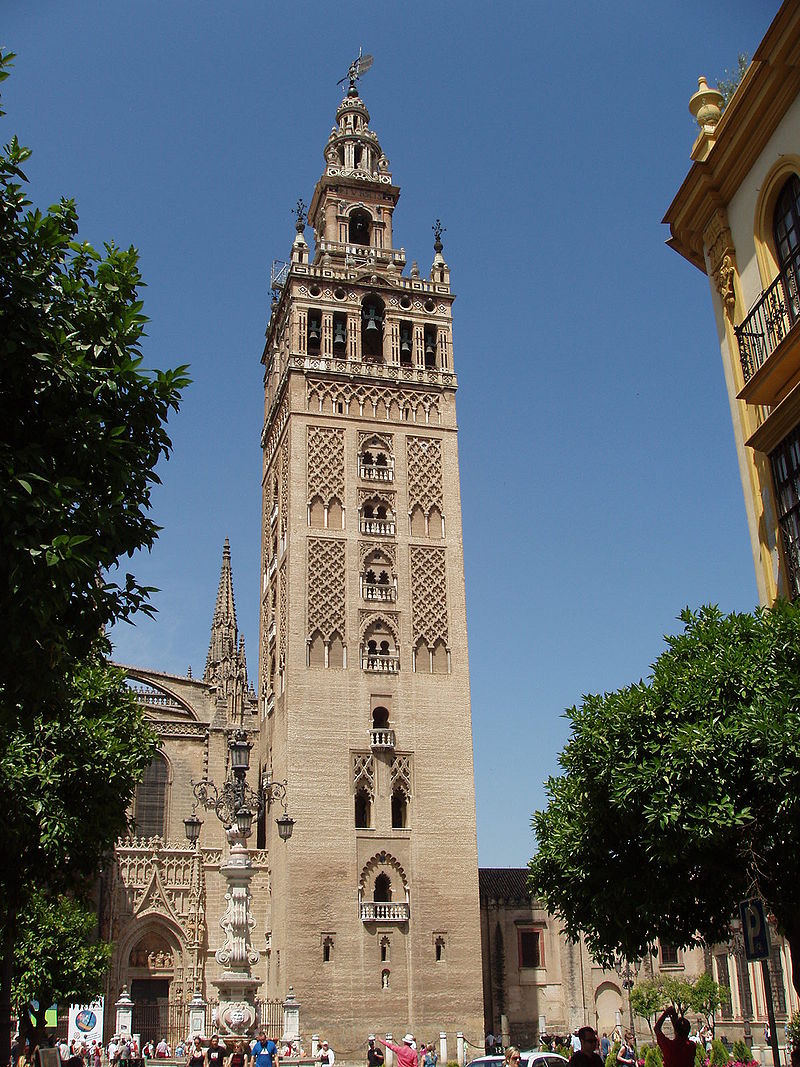

Giralda_de_Sevilla almohad Berbere dynasty
The Berber Merinid Dynasty & the Spanish & Portuguese Conquests
But the Christian states of Spain and Portugal unite and prepare for the Reconquista. The great cities of Al Andalus fall: Cordoba in 1236, Seville in 1248. Fez and Meknes are conquered by the Merinids in 1248. Marrakech is also invaded by the Merinids in 1269, which marks the end of the Almohad Berber Empire.
The Merinides Dynasty originated from the Berber Zenet tribes. They originated from Tafilalet in southern Morocco but occupied the Rif in the north, due to the weakness of the Almohads. Like the Almohads, the Merinids are interested in art. They built many medersas (Koranic schools/universities) such as the Attarine, Seffarine or Bou inania medersas in Fez.
The Portuguese and Spanish invaded several cities on the Moroccan coast : Tetouan in 1399, Ceuta in 1415, Tangier in 1471. The foreign invaders complete the Berber dynasties which divide definitively. The Merinids represent the last Berber dynasty in Morocco.
Discover the Article Gardens of Marrakech | Exoticism and Poetry
manuscrit Cantigas_bataille de la reconquista
3f/ The Berbers in Morocco from the 16th to the 20th century
The Saadian Cherifian Dynasty
The Saadian dynasty is Cherifian (descendant of the Prophet), originally from Arabia. Settled in Tamegroute in the Draa Valley (near the Moroccan Sahara), this family imposed itself following its victory against the Portuguese occupera in 1541 with the recapture of Agadir. Eastern Morocco is under Ottoman domination with the regency of Algiers, but the power of the Saadian Sultan Ahmed el Mansour is confirmed by the pre-eminence of the Saadian Caliphate and its powerful army. Morocco also annexes Timbuktu to Mali in order to get its hands on the gold minerals. Ahmed el Mansour died of the plague in 1603. His succession will lead to a power struggle.
The Alaouite Cherifian Dynasty
The Alaouite Cherifian dynasty originates from the Arabian Peninsula, near Medina, and comes from Tafilalet in south-eastern Morocco, at the entrance to the Sahara. Far descendant of the Prophet Ali, it took power over the Saadians in 1659. She subdues the rebellious Berber tribes in the south towards Marrakech. In the 18th century and early 19th, Morocco is shaken by dynastic crises and secessions on the part of the Berber Rifans and the Middle Atlas around 1810.
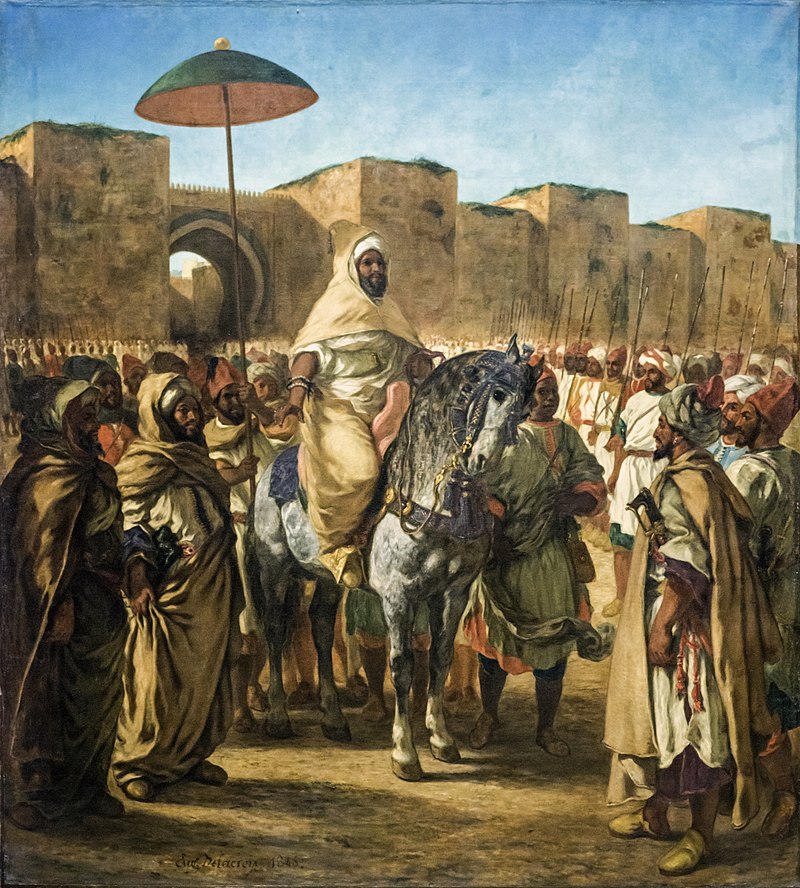
Overall, the Alaouite dynasty strengthened the Moroccan state, fighting against the invasion attempts of the Ottoman Empire and the residence of Algiers, and attacks from Spain. Sultan Abderrahmane ben Hicham, painted by Eugene Delacroix in 1845, brings Morocco out of its isolation. The Sultan of Morocco also came to the aid of the Emir of Algiers, Abdelkader, in 1839, as a result of French views on Algeria (1830). He declared war on France in 1844.
Discover the Article Hammam in Marrakech History of a Long Lasting Tradition
abderrahmane ben hicham Le_Sultan_du_Maroc_-_Eugène_Delacroix 1845
French & Spanish occupation
But the defeat of Morocco at the Battle of Isly marks the beginning of the future French takeover of the Cherifian kingdom. It is indeed the time of modern European colonialism. The defeat in the war with Spain in 1859 will ruin Morocco, which will have to pay heavy compensation. In 1894, a very young Sultan, Abdelaziz ben Hassan, came to the throne. His regency was exercised by the Vivier Ba Hmad, who commissioned the Bahia Palace in Marrakech. In 1907 France occupied Casablanca. With the Treaty of Fez signed on March 30, 1912, the Franco-Spanish protectorate is established (France in Rabat, Spain in Tetouan).
Resistance of Berbers in Morocco
As of this year, an armed Berber Amazigh resistance is being set up in Morocco. The Berber Ahmed Al Hiba confronts in 1912 the French General Mangin near Marrakech. Another Berber Hammou Zayani won the battle of Elhri against the settlers. In the Rif, the Berber tribes led by Abdelkrim El Kattabi lead the Rif War from 1921 to 1926 and a Rif republic will be established. A Moroccan nationalist movement was formed in the 1930s. France was then forced to give Morocco its independence in 1956.
Discover the Article Area Neighbourhoods of Marrakech: Gueliz Medina Palmeral
Berbere Marocain Mohammed ben Abdelkrim el-KhattabiNo room was left for ethnic minorities during decolonization, despite the important role of Berbers in armed resistance against the settlers, particularly in the Rif region. Berbers are marginalized by foreign forces.
4/ The Berbers in Morocco Today
4a/ The Plural History
The numerous invasions and colonizations of North Africa and Morocco in particular since the Phoenicians have always given way to the culture of indigenous ethnic groups. Under the Romans or the Arabs, the local populations have always managed to keep their culture. Romanization and Arabization have not been complete or total. Islam and the Arabic language have served as a catalyst to unify the Moroccan people.
During periods of expansion, the Berber ethnic groups played a major role : invasion of Spain in 711, uprisings against the Arabs in 741 and great Moorish Almoravid and Almohad Berber dynasties conquering in the 11th and 12th centuries. In Al Andalus, the Arabic language constituted a “supra nationality” integrating Jews, Christians, Muslims and a majority of Berbers. These populations thus preserved their ethnic characteristics. Interculturality allowed a profusion of creativity conducive to the development of an exceptional civilization. Andalusia is the leading tourist region in Spain with an invaluable Moorish Arab-Berber heritage.
Discover the Article Maps of Marrakech | To Print and Download
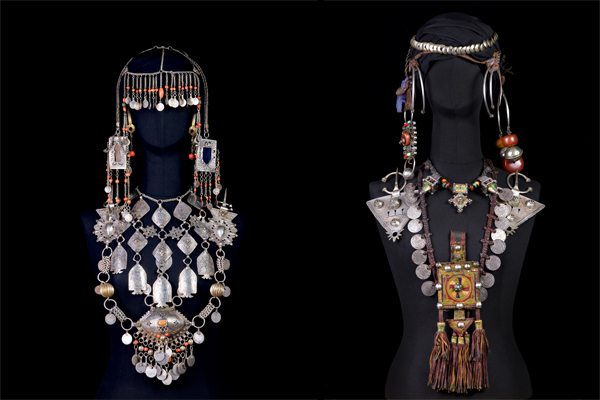
Parure Bijoux berbère-© fondation-pierre-berge-yves-saint-laurent-femmes-berberes-du-maroc
4b/ Being Moroccan & Berber in Morocco
In the 20th century, Berber resistance under the French protectorate, especially during the Rif War, was fundamental to independence. It served the cause of an entire nation, dominated and seeking to regain its autonomy. It was also the event of the “Berber Dahir” of 1930, a regulation by which the French attempted to split the Moroccan people in two, which led to a strong protest against the French occupier. With the Arabs on one side and the Berbers on the other, this Dahir marked the beginning of Moroccan nationalism that led to independence.
The Berbers in Morocco today are therefore an inseparable component of Moroccanness. The history and culture of Berber origin remain a wealth for Morocco, as Al Andalus is for Spain. This culture is also a major vector in terms of tourism, an important part of the Moroccan economy, with its magnificent Berber villages terraced in the Atlas, its handicrafts or art with its Amazigh graphic signs.
4c/ Contemporary Berberity
SM Mohamed VI materialized it in 2001. That same year, the King of Morocco founded IRCAM, the Royal Institute of Amazigh Culture, by Dahir (royal decree), in order to safeguard and promote Amazigh at the social, cultural and media levels. The mother of HM Mohamed VI, in power since 1999, Lalla Latifa, is a Berber Amazigh from Khenifra.
Subsequently, during the Arab spring in 2011, a new constitution establishes the Berber Amazigh Moroccan standard language as the official language. Article 5 of the Moroccan constitution of 2011 then recognizes Amazigh as “official language and common heritage of all Moroccans“. Algeria officializes Amazigh in 2016.
Morocco, which has experienced many influences throughout history, has always been able to maintain a very strong autonomy of its indigenous population. This has allowed the Berber ethnic groups to participate strongly in the founding of the nation, or to resist. The Civilization of the Berber Ethnic Groups in Morocco, with more than 10,000 years of existence, as old as that of the Pharaohs of Egypt, constitutes the DNA of the Cherifian Kingdom. Berberity is an indelible marker of North African societies.
Discover the article Things to Do in Marrakech – What To Visit ?

femme Amazigh en habit traditionnel berbere

Spa & Riad Marrakech Al Ksar
Visit Le Spa of Riad Al Ksar in the Médina : Hammam & Massage for Couples
Practical Information :
Berber Museum in Majorelle garden. Entrance Fee: 100dhs. Open Everyday except Boxing Day & New Year
The following Articles may interest you:
Jemaa El Fnaa Square Marrakech | History and Culture
How To Get Around Marrakech | Taxi Bus Train Airport Transfer Scooter Car Ticket Fare
Koutoubia Mosque Marrakech Morocco | History & Architecture
Bahia Palace Marrakech | 19th Century Masterpiece
Majorelle Garden in Marrakech | a Moroccan Love Story
Monuments to Visit in Marrakech
©alksar 2020 – https://www.alksar.com
Bibliography
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berb%C3%A8res
https://www.lhistoire.fr/il-%C3%A9tait-une-fois-les-berb%C3%A8res